Glycemic Index and Impact on Blood Sugar
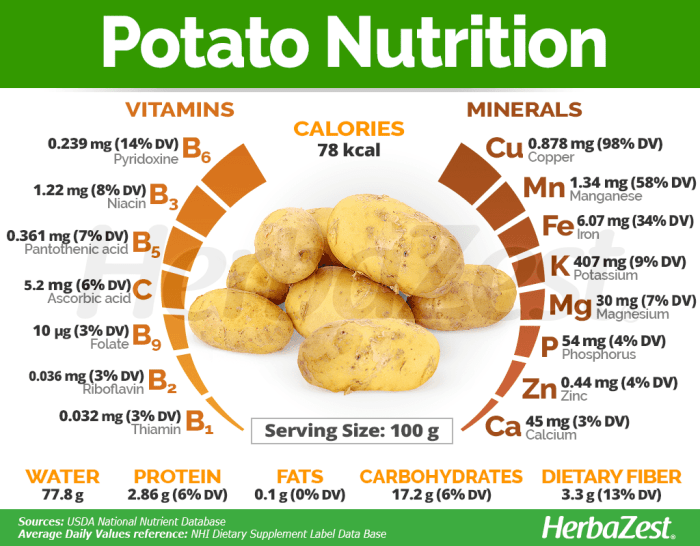
Russet potato nutrition facts – Russet potatoes, a staple in many cuisines, have a significant impact on blood sugar levels due to their carbohydrate content. Understanding the glycemic index (GI) of russet potatoes and how different cooking methods affect it is crucial for managing blood sugar, particularly for individuals with diabetes or those aiming to maintain healthy blood sugar levels.The glycemic index is a ranking system for carbohydrate-containing foods based on how quickly they raise blood glucose levels after consumption.
A higher GI indicates a faster and more significant rise in blood sugar. Russet potatoes, in their raw state, possess a moderate to high GI. However, the GI value can fluctuate considerably depending on several factors, primarily the cooking method employed.
Effect of Cooking Methods on Russet Potato GI
The cooking method significantly influences the GI of russet potatoes. Boiling tends to increase the GI compared to baking or steaming, as boiling breaks down the cell structure of the potato more rapidly, making the starch more readily available for digestion and absorption. Frying, on the other hand, further elevates the GI due to the formation of acrylamide, a compound associated with increased blood sugar response.
Baking or microwaving generally results in a lower GI compared to boiling or frying, as these methods retain more of the potato’s fiber and cell structure. The presence of fat during frying also impacts digestion and absorption rates.
Comparison of Glycemic Index Across Potato Varieties
The following table compares the glycemic index of russet potatoes with other common potato varieties. Note that GI values can vary depending on factors like growing conditions, potato maturity, and specific cooking methods. These values represent approximate averages.
| Potato Variety | Glycemic Index (GI) | Typical Cooking Method | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Russet (baked) | 80-90 | Baked | GI can vary based on baking time and temperature |
| Russet (boiled) | 90-110 | Boiled | Boiling increases the GI compared to baking |
| Red Potatoes (boiled) | 70-80 | Boiled | Generally lower GI than russet potatoes |
| Yukon Gold (boiled) | 70-80 | Boiled | Similar GI to red potatoes |
Russet Potato vs. Other Potato Types

Russet potatoes, known for their fluffy texture when baked or mashed, are just one variety among many. Understanding the nutritional differences between russet and other popular potato types can help you make informed choices for your diet. This section will compare and contrast russet potatoes with red potatoes and sweet potatoes, highlighting key nutritional variations and their implications for different dietary needs.
Several factors influence the nutritional profile of potatoes, including variety, growing conditions, and preparation methods. While all potatoes offer some nutritional value, their composition varies significantly. This variation is particularly noticeable when comparing russet potatoes to other popular types such as red potatoes and sweet potatoes.
Nutritional Differences Between Potato Types
The following bullet points highlight key differences in nutritional content between russet, red, and sweet potatoes. These differences can significantly impact their suitability for various dietary goals, such as managing blood sugar levels or increasing dietary fiber intake.
- Starch Content: Russet potatoes are higher in starch than red potatoes, contributing to their higher glycemic index. Red potatoes have a lower starch content and a lower glycemic index. Sweet potatoes, while also starchy, have a more complex carbohydrate structure which affects their glycemic response differently than russet potatoes.
- Fiber Content: Red potatoes generally contain more fiber than russet potatoes. Sweet potatoes boast a considerably higher fiber content than both russet and red potatoes. This higher fiber content can aid in digestion and promote feelings of fullness.
- Vitamin and Mineral Content: Sweet potatoes are particularly rich in beta-carotene (which converts to vitamin A), vitamin C, and manganese. Red potatoes offer a good source of vitamin C and potassium. Russet potatoes also contain potassium and vitamin C, but in lower amounts compared to red and sweet potatoes.
- Glycemic Index (GI): As previously discussed, russet potatoes have a higher GI than red potatoes. Sweet potatoes have a moderate GI, often lower than russet but higher than red potatoes, depending on the preparation method.
Nutritional Comparison Table, Russet potato nutrition facts
The table below summarizes the key nutritional differences (per 100g cooked) between russet, red, and sweet potatoes. Note that these values can vary slightly depending on growing conditions and preparation methods.
| Nutrient | Russet Potato | Red Potato | Sweet Potato |
|---|---|---|---|
| Calories | ~90 | ~80 | ~90 |
| Carbohydrates (g) | ~20 | ~18 | ~20 |
| Fiber (g) | ~2 | ~3 | ~3 |
| Vitamin C (mg) | ~10 | ~20 | ~10 |
| Potassium (mg) | ~400 | ~400 | ~350 |
| Vitamin A (µg) | ~0 | ~0 | ~1000 |
Health Benefits and Potential Drawbacks
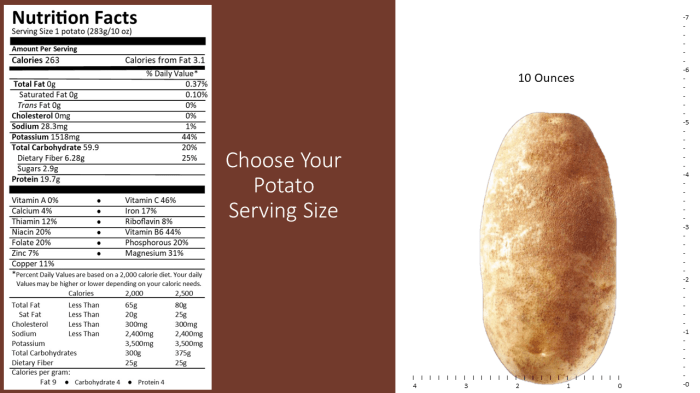
Russet potatoes, while often associated with high carbohydrate content, offer a range of nutritional benefits when consumed as part of a balanced diet. However, excessive consumption can also lead to certain drawbacks. Understanding both the advantages and disadvantages is crucial for incorporating them effectively into a healthy eating plan.Russet potatoes are a good source of several essential nutrients. Their nutritional profile contributes to various aspects of health and well-being, but moderation is key to maximizing benefits and minimizing potential negative effects.
Nutritional Benefits of Russet Potatoes
Russet potatoes provide a significant amount of potassium, a vital mineral that plays a crucial role in maintaining healthy blood pressure. They also contain vitamin C, an antioxidant that supports the immune system and collagen production. Furthermore, they are a source of vitamin B6, important for brain development and function, and dietary fiber, which aids digestion and promotes satiety.
The fiber content contributes to feelings of fullness, which can be beneficial for weight management. Finally, russet potatoes offer small amounts of other vitamins and minerals, contributing to overall nutritional intake.
Potential Drawbacks of Excessive Russet Potato Consumption
The high carbohydrate content of russet potatoes is a primary concern, especially for individuals with diabetes or those managing their blood sugar levels. A large portion of russet potatoes can lead to a rapid spike in blood glucose, potentially causing negative health consequences. Furthermore, the preparation method significantly impacts the nutritional value and glycemic index. Fried russet potatoes, for instance, add unhealthy fats and increase the glycemic load compared to baked or boiled potatoes.
Excessive consumption can also contribute to weight gain if not balanced with adequate physical activity and a healthy overall diet. It is important to note that these drawbacks primarily relate to overconsumption; moderate intake as part of a balanced diet typically poses no significant health risks.
Healthy Ways to Incorporate Russet Potatoes into a Balanced Diet
Incorporating russet potatoes into a healthy diet requires mindful preparation and portion control. Here are some examples of healthy ways to include them in your meals:
- Bake them in their skins with herbs and spices instead of frying. This retains more nutrients and avoids added unhealthy fats.
- Use them as a base for hearty stews or soups, adding vegetables and lean protein for a balanced and nutritious meal.
- Mash them with a small amount of milk or broth, adding flavor with herbs and spices, instead of using excessive amounts of butter or cream.
- Roast them with other vegetables for a side dish that is both flavorful and nutritious.
- Include them in a balanced breakfast, perhaps as part of a potato hash with other vegetables and lean protein.
Essential FAQs: Russet Potato Nutrition Facts
Are russet potatoes a good source of potassium?
Yes, russet potatoes are a good source of potassium, an essential mineral for maintaining healthy blood pressure.
Can I eat russet potatoes if I have diabetes?
Individuals with diabetes should consume russet potatoes in moderation and be mindful of portion sizes due to their carbohydrate content. Boiling or baking is preferred over frying to lower the glycemic impact.
How can I reduce the glycemic index of russet potatoes?
Boiling or baking russet potatoes, as opposed to frying, and consuming them with fat and protein can help to lower their glycemic index.
Are there any antioxidants in russet potatoes?
Yes, russet potatoes contain various antioxidants, although the levels may vary depending on factors like growing conditions and preparation methods.
Are russet potatoes suitable for weight loss diets?
Russet potatoes can be included in weight loss diets, but portion control is essential due to their carbohydrate content. Choosing healthy preparation methods and incorporating them as part of a balanced meal plan is key.
